Shoulder Labral Tear
Labral Tear of Shoulder
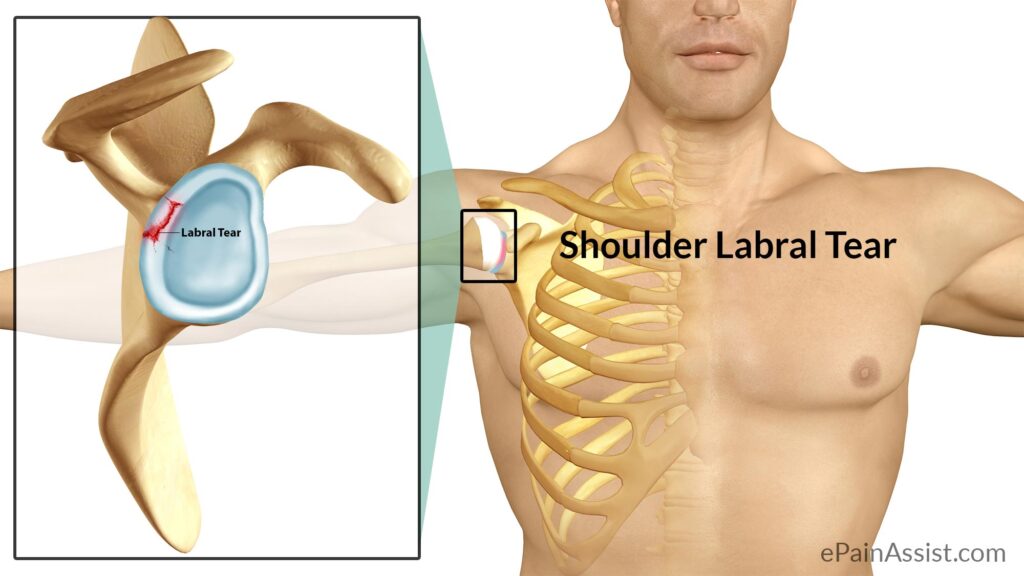
A labral tear is a type of injury that can occur in the shoulder. It is often caused by a rotator cuff tear and can lead to considerable pain and loss of motion. If you have been diagnosed with a labral tear, this guide will provide you with information on what to expect and how to recover.
Labral Tear: An introduction
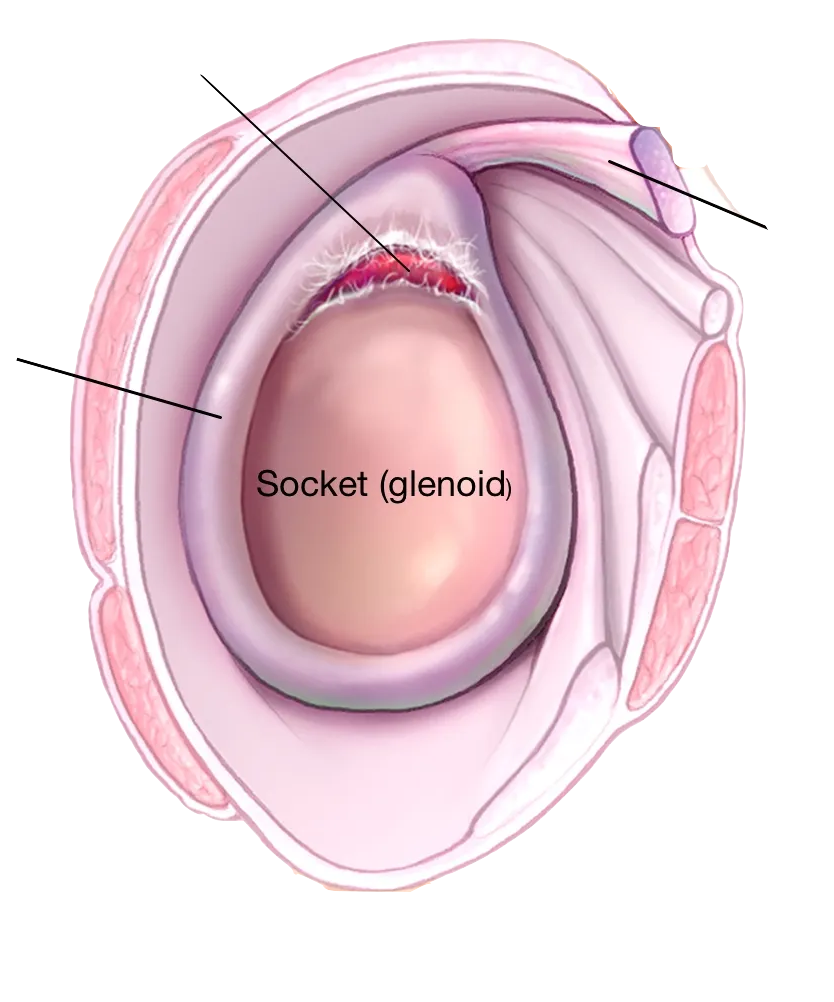
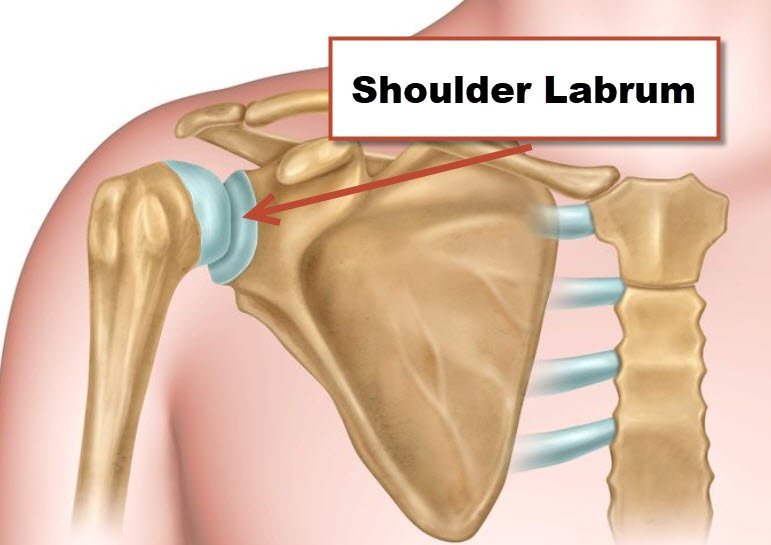
A labral tear is a common shoulder injury. The shoulder is a ball-and-socket joint that is held together by a number of different muscles, ligaments, and tendons. The labrum is a piece of cartilage that lines the socket of the shoulder joint and helps to keep the ball in place.
A tear in the labrum can cause pain and instability in the shoulder joint.
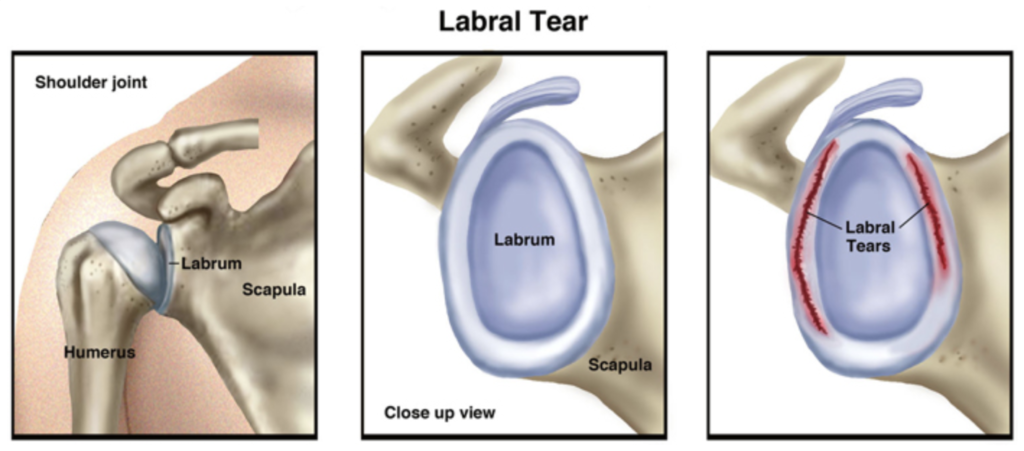
Causes of Labral Tears in shoulders
Labral tears are most often caused by overuse or repetitive motion, such as from throwing a baseball or tennis. They can also be caused by trauma, such as a fall on an outstretched arm. People who participate in overhead activities, such as swimming or weightlifting, are also at higher risk for developing a labral tear.
Symptoms of a Labral Tear
The most common symptom of a labral tear is a sharp pain in the shoulder. This pain is usually worse with movement and may be accompanied by a clicking or popping sensation. Other symptoms may include:
– Difficulty moving the arm
– Weakness in the arm
– Instability in the shoulder
Risk Factors for a Labral Tear
The most common risk factor for developing a labral tear is participating in activities or sports that put repetitive stress on the shoulder joint, such as baseball, tennis, or weightlifting. Other risk factors include:
-Previous shoulder injury or surgery
-Osteoarthritis in the shoulder joint
-Dislocation of the shoulder joint
-Loose or torn ligaments in the shoulder joint
-Bone spurs in the shoulder joint
-Instability in the shoulder joint
If you have any of these risk factors, it is important to talk to your doctor or orthopedic specialist about ways to help prevent a labral tear.
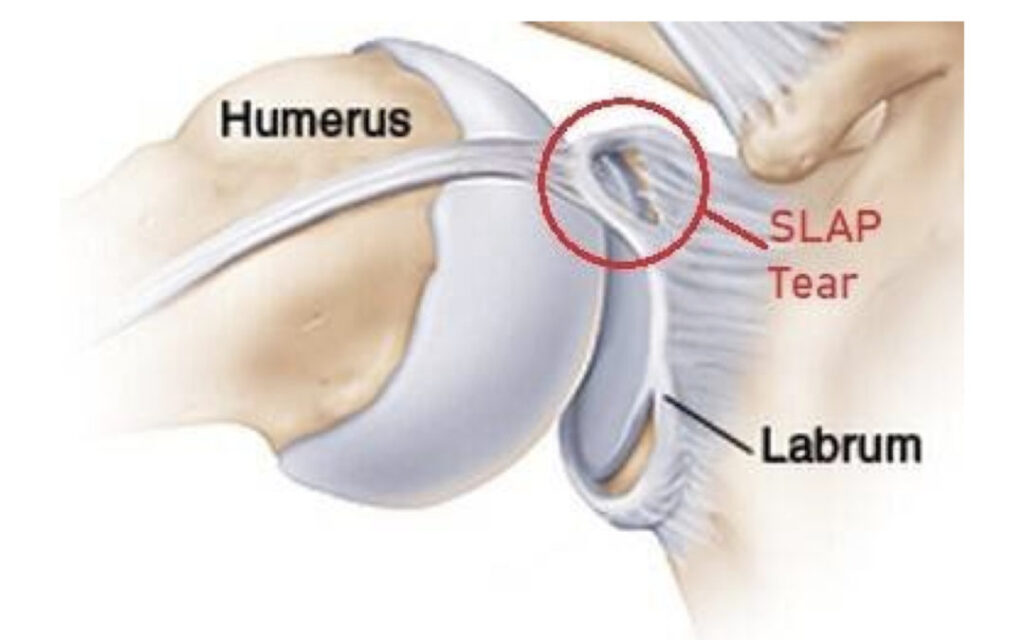
Diagnosis of Labral Tear
Diagnosis of a labral tear is typically done with an MRI. Your doctor will look for signs of a tear, such as loss of cartilage or fluid in the joint. He or she may also order X-rays to rule out other causes of your symptoms, such as arthritis. If your doctor suspects you have a tear but the MRI is inconclusive, he or she may recommend an arthroscopy. This is a minimally invasive surgery in which a small camera is inserted into the shoulder joint to look for signs of a tear.
Treatment options for a Labral Tear
Treatment options for shoulder or hip labral tears may vary depending on the severity of your tear. If you have a small or moderate tear, your doctor may recommend pain relievers and anti-inflammatory medication. They may also suggest physical therapy to help strengthen the muscles around your hip joint. If you have a large or complete tear, you may need surgery to repair the damage. Surgery can be done arthroscopically, which is a minimally invasive procedure, or open, which is more traditional surgery.
Recovery times vary depending on the type of surgery you have, but typically, it takes several months to fully recover.
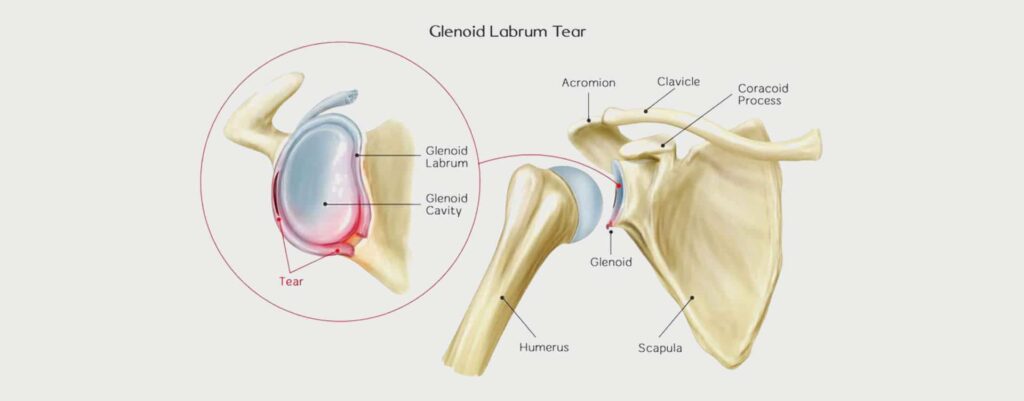
The long-term outlook for a labral tear patient
There is no one-size-fits-all answer to this question, as the long-term outlook for someone with a labral tear will vary depending on the individual’s age, overall health, and the severity of their injury. However, it is generally agreed that early diagnosis and treatment of a torn hip labrum or shoulder labrum can improve the chances of a full recovery. In some cases, surgery may be required to repair the damage. Physical therapy may also be recommended in order to help strengthen the muscles and joints around the affected area. With proper treatment, most people who suffer from a labral tear are able to return to their previous level of activity and enjoy a good quality of life.
How can you prevent a labral tear from occurring in the first place?
There are a few things you can do to help prevent a shoulder or hip labral tear from occurring:
- Use good form when lifting weights and participating in other activities that put stress on the shoulder joint.
- Avoid activities that require repetitive overhead motions of the arm, such as tennis or swimming.
- Strengthen the muscles around the shoulder joint to help support the joint and reduce stress on the labrum.
- Stretch the muscles and tissues around the shoulder joint regularly to keep them flexible and reduce strain on the labrum.
If you do experience a shoulder injury that results in pain, it is important to see a doctor or orthopedic specialist so they can properly diagnose and treat the problem. Early intervention can help prevent a more serious injury from occurring.
Frequently Asked Questions
Yes, hip and shoulder labral tears are different. The hip is a ball-and-socket joint, while the shoulder is a glenohumeral or hinge joint. The function of the labrum in each joint is also different. In the hip, the labrum deepens the socket and helps to stabilize the ball in the socket. In the shoulder, the labrum acts as a cushion between the head of the humerus (upper arm bone) and the glenoid (shoulder blade). Patients with a hip labral tear feel pain in different areas of the body when compared with patients of shoulder labral tears.
There are several possible causes of hip labral tears, including:
- Trauma: A direct blow to the hip can injure the labrum.
- Overuse: Repetitive stress on the hip joint can cause the labrum to tear. This is common in athletes who participate in sports that require a lot of twisting and turning, such as soccer, hockey, and golf.
- Dislocation: A dislocated hip can stretch or tear the labrum. Deformity of the femoral head can also be a cause of pain in the hip socket.
- Hip impingement: This condition occurs when the bones of the hip joint rub against each other, causing the torn labrum to become irritated and inflamed. Hip impingement or hip dysplasia can be caused by a structural abnormality, such as a shallow socket or an overgrowth of bone.
The most common symptom of a hip labral tear is pain. The hip pain may be sharp and severe, or it may be a dull, aching hip or groin pain. The pain may radiate from the hip to the groin, thigh bone, or buttock. Other symptoms may include:
- Clicking, popping, or grinding sounds when the hip is moved
- Stiffness or loss of range of motion in the hip joint
- Instability or giving way of the hip joint
A hip labral tear is typically diagnosed using imaging tests, such as an MRI or CT scan. These tests can help to visualize the structures of the hip joint and look for signs of injury to the labrum. Your doctor may also order X-rays or hip arthroscopy to rule out other conditions, such as arthritis or a fracture.
Hip labral tear treatment may vary depending on the severity of the injury. To treat labral tears of mild nature, your doctor may recommend conservative treatment, such as rest, ice, and physical therapy. Physical therapy can help to strengthen the muscles around the hip joint and improve range of motion. If conservative treatment does not relieve your symptoms, your doctor may recommend hip labral tear surgery to repair the tear of the hip.
3 Ways to Level Up Your Rehab and Injury Prevention With Us





