Achilles Tendonitis
Achilles Tendonitis
If you are an athlete or someone who leads an active lifestyle, there is a good chance you have heard of Achilles tendonitis. This condition can be extremely frustrating and lead to a great deal of pain and discomfort. In this blog post, we will discuss what Achilles tendonitis is, the symptoms you should look out for, and how to treat it. We hope this information helps you stay healthy and active!
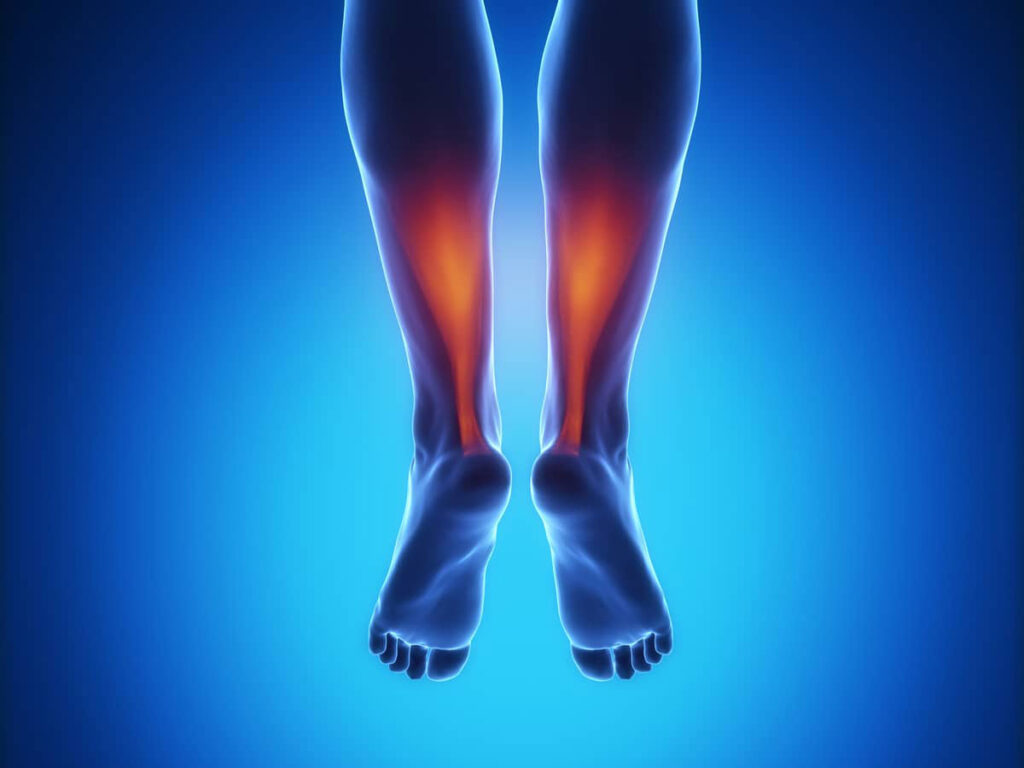
What is Achilles tendonitis?
Achilles tendonitis is a condition that results in the inflammation of the Achilles tendon, which is the large tendon located at the back of the ankle. Achilles tendonitis can be caused by overuse or repetitive stress on the Achilles tendon, or it can occur as a result of an injury.
Symptoms of Achilles tendonitis
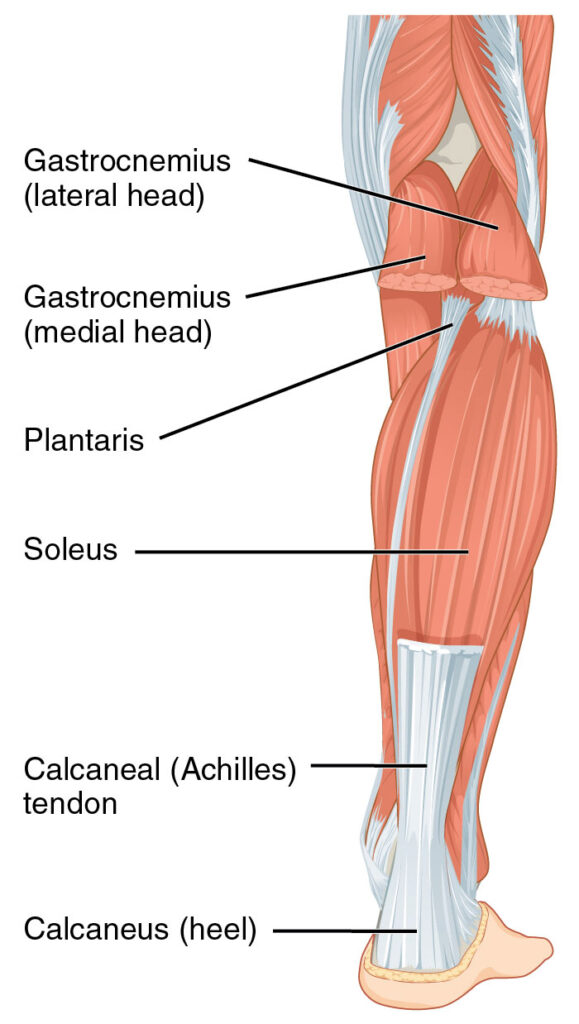
Achilles tendonitis is an inflammation of the Achilles tendon, the large cord that connects the calf muscles to the heel bone. Achilles tendon ruptures can occur suddenly, or it can develop slowly over time.
Symptoms of Achilles tendonitis include:
– Pain and stiffness in the back of the leg, above the heel
– Pain that gets worse with activity, such as walking or running
– Swelling in the area
– Warmth in the area
– Redness in the area
If you think you have Achilles tendonitis, it's important to see a doctor. Achilles tendonitis can lead to a rupture of the Achilles tendon. A complete tear of the Achilles tendon is a serious injury that requires immediate medical attention.
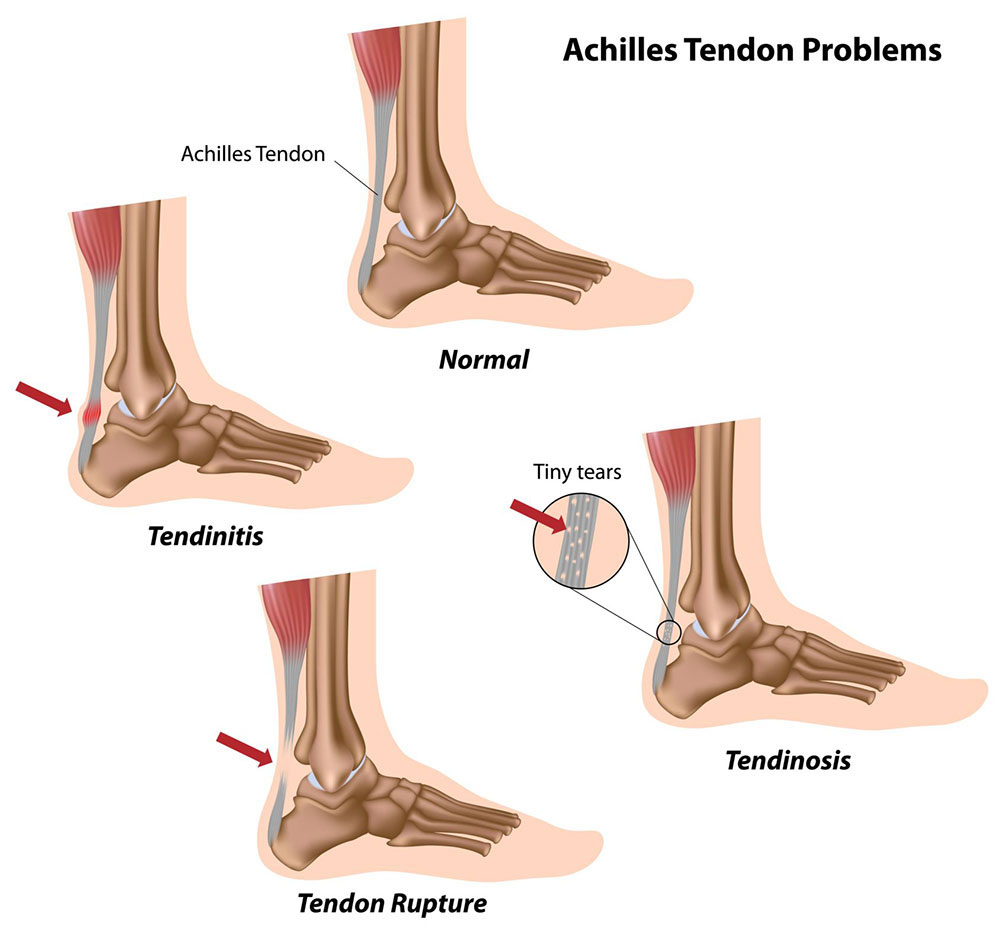
Causes of Achilles tendonitis
Achilles tendonitis is a condition that can be caused by overuse or injury to the Achilles tendon. The Achilles tendon is the large tendon that runs down the back of the leg and connects the calf muscle to the heel bone. Achilles tendonitis can occur when the tendon is subjected to repetitive stress, such as from running or jumping. This type of stress can cause the tendon to become inflamed, resulting in pain and stiffness. In some cases, Achilles tendonitis can also be caused by an injury to the tendon, such as a tear or rupture.
Treatment for Achilles tendonitis
Treatment for Achilles tendonitis can vary depending on the severity of the condition.
Mild to moderate cases:
For treating Achilles tendinitis of mild to moderate nature, measures may include:
– Resting the injured foot and ankle as much as possible
– Applying ice to the injured area for 20 minutes several times a day
– Taking over-the-counter pain relievers such as ibuprofen or aspirin
– Doing calf stretches and exercises to strengthen the muscles around the Achilles tendon
– Wearing a heel insert or orthotic device in your shoe
– Wearing a boot or cast for a short period of time to immobilize the injured area
Severe cases:
For more severe Achilles tendonitis, treatment may include:
– Physical therapy to help stretch and strengthen the Achilles tendon
– Steroid injections to reduce pain and inflammation
– Achilles tendinitis surgery to remove damaged tissue or repair the Achilles tendon
If you have Achilles tendonitis, it is important to follow your treatment plan. If the condition is not treated properly, it can lead to a tear or Achilles tendon rupture.
Prevention of Achilles tendonitis
Achilles tendonitis is a condition that results when the Achilles tendon, which connects the calf muscle to the heel bone, becomes inflamed. Achilles tendonitis can occur as a result of overuse or injury. Symptoms of Achilles tendonitis include pain and stiffness in the back of the lower leg. Treatment for Achilles tendonitis typically involves resting the affected leg, icing the area, and taking anti-inflammatory medication. In some cases, physical therapy may also be recommended.
Some simple steps that can be taken to help prevent Achilles tendinitis include:
-Wearing proper footwear that provides good support and cushioning
-Stretching the calf muscles regularly
-Avoiding activities that place undue stress on the Achilles tendon
-Increasing activity levels gradually to avoid overstressing the Achilles tendon.
If you experience any pain or discomfort in the back of your lower leg, be sure to see a doctor or other healthcare provider to rule out Achilles tendonitis or other conditions.
Frequently Asked Questions about Achilles tendonitis
The most common symptom of Achilles tendonitis is pain in the back of the leg near the heel. The pain may be mild at first and worsen with continued activity.
Other symptoms may include stiffness, swelling, and warmth in the affected area.
Achilles tendonitis is typically diagnosed based on a medical history and physical examination.
Imaging tests, such as X-rays or an MRI, may be ordered to rule out other conditions.
Treatment for Achilles tendonitis may include rest, ice, and over-the-counter pain medications.
Physical therapy exercises may also be recommended to stretch and strengthen the Achilles tendon.
In severe Achilles tendon disorders, Achilles tendon surgery may be necessary to repair the Achilles tendon rupture.
A tendinitis surgery is typically performed as an outpatient procedure. During the surgery, the surgeon will make an incision in the back of the leg and then detach the Achilles tendon from the place where the Achilles tendon attaches to the heel bone. The damaged portion of the tendon will be removed and then repaired. The incision will be closed with stitches.
The recovery time for Achilles tendonitis surgery is typically 6-8 weeks. Physical therapy may be recommended to help with the recovery process.
There are two types of Achilles tendinitis:
– Noninsertional Achilles Tendinitis
– Insertional Achilles Tendinitis
Risks of Achilles tendonitis surgery include infection, blood clots, and nerve damage. There is also a risk that the Achilles tendon may not heal properly after surgery.
Achilles tendinopathy is an overuse injury of the Achilles tendon, the band of tissue that connects calf muscles to your heel bone. Achilles tendinosis is a degenerative condition caused by repetitive or prolonged stress on the Achilles tendon. The term “tendinosis” refers to the degeneration of collagen fibers within the tendon.
Have you been injured at some point in your journey?
Are you not achieving your highest level of function?
We’ve helped hundreds of people at all walks in life
get back to performing their best painfree!
3 Ways to Level Up Your Rehab and Injury Prevention With Us





