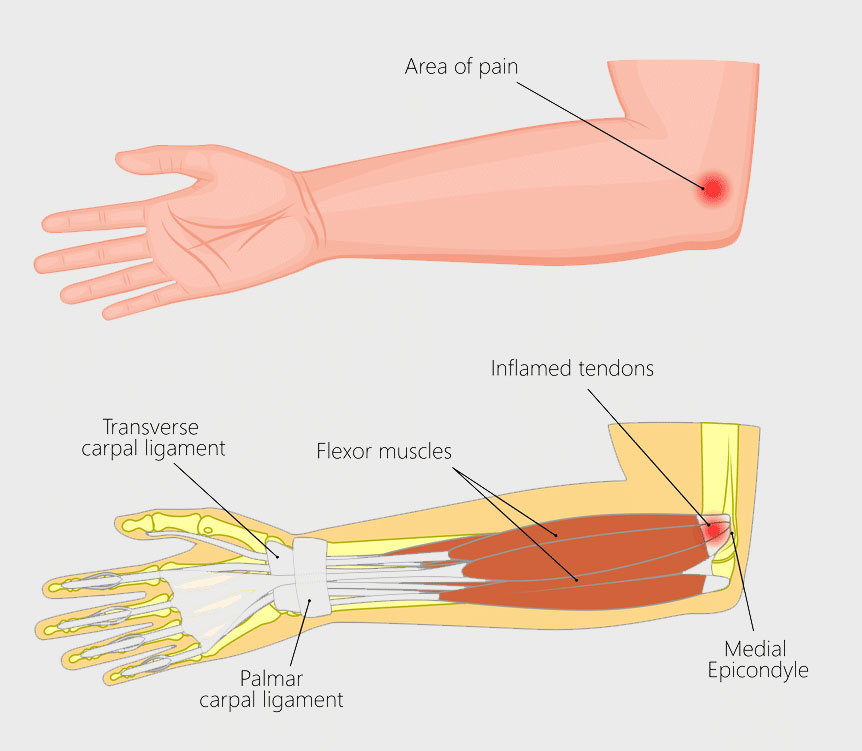
Golfer’s Elbow (Medial Epicondylitis)
Golfers Elbow
Did you know that there is a condition called golfers elbow? It’s a type of tendinitis that is caused by repetitive motions of the arm and elbow, such as those often used in golf. If you are experiencing pain and inflammation in your elbow, chances are you may have a golfer’s elbow. Check out this post for more information on the condition and how to treat it.
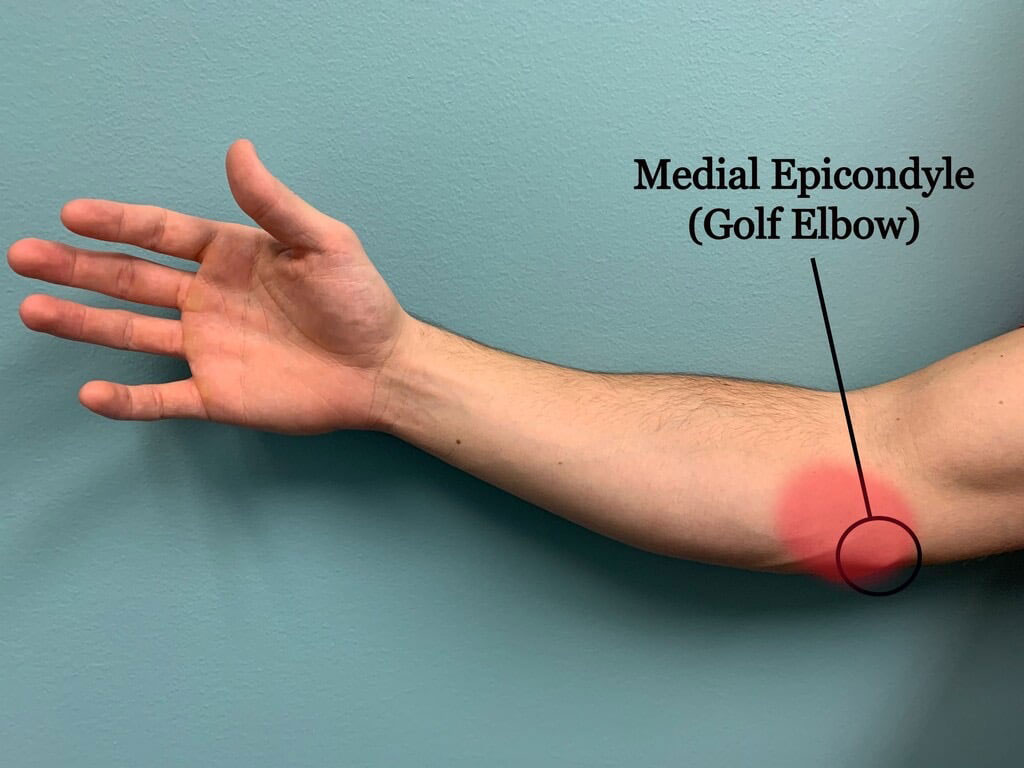
What is a golfers elbow?
Golfer’s elbow or medial epicondylitis is a type of tendonitis that affects the tendons in the elbow. It is a common injury among golfers, but can also occur in other athletes who use their arms repetitively. Sometimes it is also referred to as the forehand tennis elbow. Symptoms include medial elbow pain and tenderness on the inside of the elbow, weakness in the forearm, and numbness or tingling in the fingers. Treatment typically involves rest, ice, and physical therapy. Surgery is rarely needed.
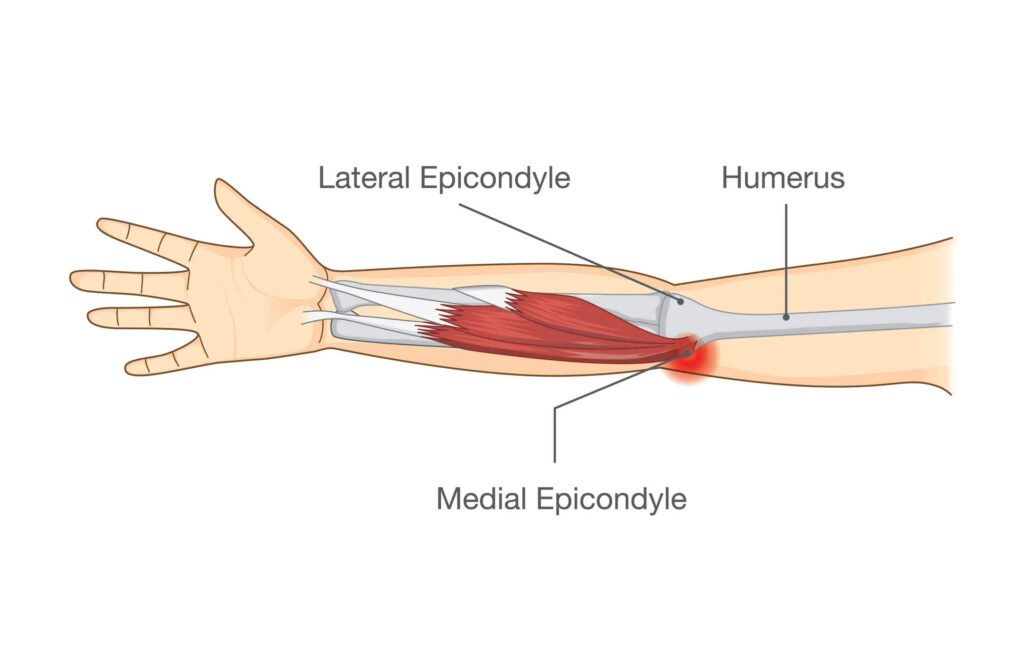
How do you know if you have a golfer's elbow?
There are a few different ways you can tell if you have a golfer’s elbow. One way is to pay attention to the pain you’re experiencing. If you have a golfer’s elbow, you’ll likely feel a sharp, shooting pain on the inside of your elbow. This pain may come and go, but it will usually be worse when you move your arm in certain ways (such as in a golf swing).
Another way to tell if you have a golfer’s elbow is to look for signs of inflammation. If your elbow is swollen, tender to the touch, or red, it’s possible that you have a golfer’s elbow. You may also notice that your range of motion is limited.
If you think you might have golfers elbow, it's important to see a doctor or other medical professional. They can perform tests to confirm the diagnosis and develop a treatment plan to help you find relief from your symptoms.
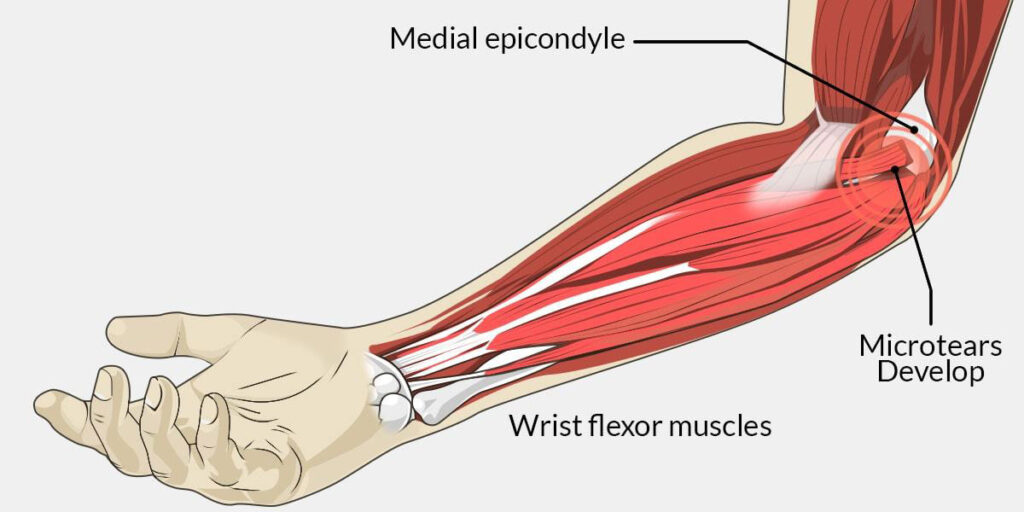
What are the causes of golfers elbow?
One of the most common causes of golfers elbow is overuse. This condition is often seen in athletes who participate in repetitive motions that put stress on the elbow joint, such as golf, baseball, and tennis.
Other causes of golfers elbow can include:
- -Injury or trauma to the elbow
- -Arthritis
- -Osteoporosis
- -Tendinitis
- -Carpal tunnel syndrome
- -Cubital tunnel syndrome
- -Radial tunnel syndrome
- -De Quervain’s disease
- -Guyon’s canal syndrome
- -Nerve entrapment syndrome
- -Ganglion cysts
- -Infection
- -Inflammation
- -Tumors
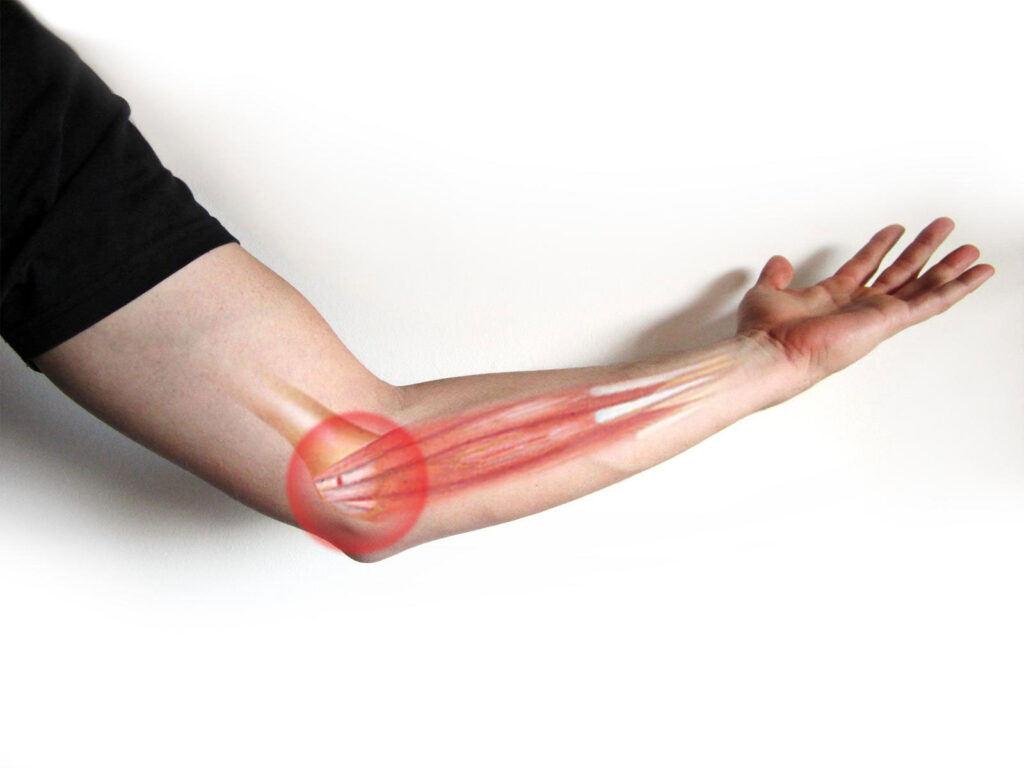
Treatment for golfers elbow
If you think you may be suffering from golfers elbow, it is important to see a doctor or medical professional for treating the golfer's elbow. They will be able to properly diagnose medial and lateral epicondylitis and recommend the best course of treatment.
Treatment for golfers elbow often includes:
- -Resting the elbow and avoiding activities that aggravate the condition
- -Ice therapy to reduce inflammation and pain
- -Heat therapy to improve blood circulation and promote healing
- -Stretching and strengthening exercises
- -Physical therapy
- -Ultrasound therapy
- -Massage therapy
- -Acupuncture
- -Anti-inflammatory medications or corticosteroid injections
- -Surgery (in severe cases)
Tips to prevent Golfer's Elbow
To prevent lateral and medial epicondylitis from happening, follow these tips:
- Use a warm-up routine before playing golf or any other physical activity.
- Strengthen your forearm muscles by doing exercises such as wrist curls and reverse wrist curls.
- Stretch your forearm muscles regularly.
- Wear a support bracelet or wrap when playing golf or engaging in any activity that puts stress on your elbow joint.
- Avoid overuse of your elbow joint by taking frequent breaks during activities that require repetitive motion.
- If you begin to experience pain in your elbow, ice the area for 20 minutes several times a day to reduce inflammation.
- Consult with a doctor or physiotherapist if the pain does not improve with self-care measures. They may recommend additional treatments such as steroid injections or surgery.
Recovery time for Golfers Elbow
Recovery time for a golfer’s elbow can vary depending on the severity of the injury. For a milder case, healing can take place within a few weeks, while more severe cases may take several months. It is important to rest the affected arm and avoid activities that aggravate the condition. Physical therapy may be recommended to help improve range of motion and strength. Surgery is generally only considered for severe cases that do not respond to other treatment methods.
Most people with Golfers Elbow will eventually make a full recovery with proper care and treatment. However, the condition can sometimes lead to chronic pain and disability if it is not managed properly. It is important to seek medical attention as soon as possible if you think you may have developed Golfers Elbow. Early diagnosis and treatment can help to speed up the healing process and reduce the risk of long-term complications.
The Boost Anti-Gravity Treadmill offered at MOTUS Specialists Physical Therapy takes the same science and tweaks it in order to do the opposite. Instead of increasing weight, it makes the user feel less weight.
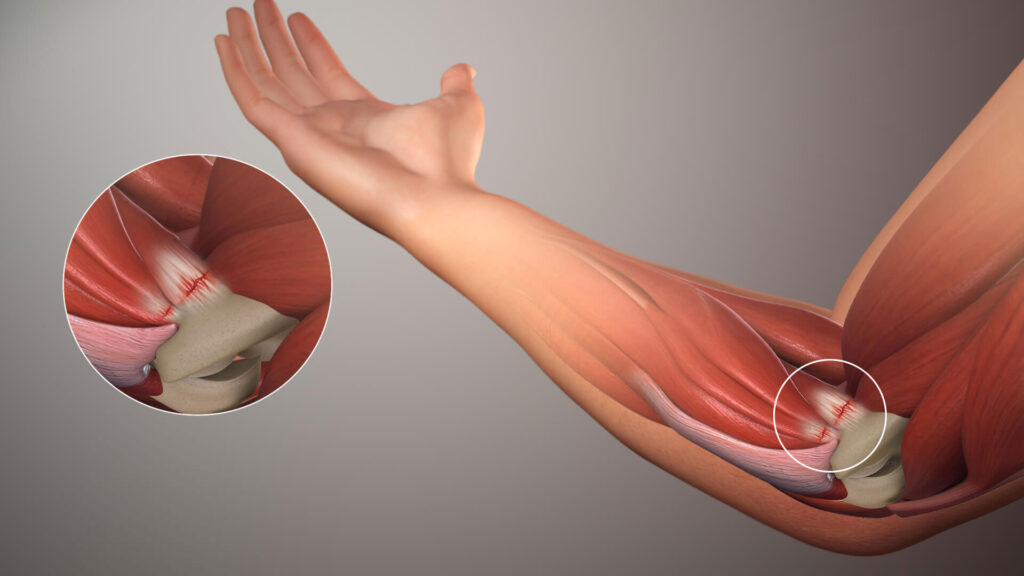
Frequently Asked Questions about Golfers Elbow
A Golfer’s elbow is a condition that causes pain in the elbow and forearm. It is caused by the overuse of the muscles and tendons in the forearm.
Anyone who overuses their forearm muscles can develop a golfer’s elbow. This includes people who play golf, tennis, and other racquet sports. It can also occur in people who do repetitive motions with their arms, such as painting or using a computer mouse.
The most common symptom of golfers elbow is pain on the inside of the elbow. A resisted wrist extension can aggravate this pain. This pain can radiate down the forearm and into the wrist. Other symptoms include tenderness, weakness, and numbness in the affected arm.
A golfer’s elbow is typically diagnosed through a combination of medical history and physical examination. Your doctor will ask about your symptoms and activities that may have caused or aggravated them. They will also examine your elbow and forearm for signs of irritation or inflammation. A resisted wrist flexion increases the pain of a patient suffering with a golfer’s elbow.
The goal of treatment for golfers’ elbows is to reduce pain and inflammation while allowing the muscles and tendons to heal. Treatment options include rest, ice, heat, ultrasound therapy, and corticosteroid injections. In some cases, surgery (medial epicondyle) may be necessary to remove damaged tissue.
Most people with golfers’ elbows recover with conservative treatment. However, the condition can recur if the initial injury is not properly healed or if the person resumes activities that put stress on the forearm muscles and tendons too soon. Surgery is usually only recommended for severe cases that do not respond to other treatments.
Have you been injured at some point in your journey?
Are you not achieving your highest level of function?
We’ve helped hundreds of people at all walks in life
get back to performing their best painfree!
3 Ways to Level Up Your Rehab and Injury Prevention With Us





